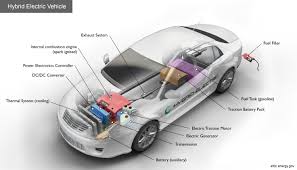
Hybrid cars use both a fossil fuel engine and electric engine, the best hybrids achieve better fuel efficiency than their non-hybrid counterparts. They also pollute less and save drivers money through fuel savings. The most advanced hybrid cars have larger batteries and can recharge their batteries from an outlet, allowing them to drive extended distances on electricity before switching to gasoline. These hybrids are known as "plug-in hybrids," these cars can offer much-improved environmental performance and increased fuel savings by substituting grid electricity for gasoline.

Like the switch that turns off your refrigerator's light bulb when the door is closed, "idle-off" is a feature that turns off your hybrid car's fossil fuel engine when the vehicle is stopped, saving fuel. The battery provides energy for the air conditioner and accessories while the vehicle idles at stoplights or in traffic, and the electric motor can start the vehicle again. If needed, the fossil fuel engine will start to provide more power for acceleration. "Regenerative braking" is another fuel-saving feature that hybrids have. Fossil fuel cars rely entirely on friction brakes to slow down, disappearing the vehicle's kinetic energy as heat. Regenerative braking allows some of that energy to be captured, turned into electricity, and stored in the batteries. This stored electricity can later be used to run the motor and move or start the hybrid. Having an electric motor also allows for more efficient engine design. Another feature is "power assist" this feature helps reduce demands on a hybrid’s gasoline engine, which in turn can be downsized and more efficiently operated. The gasoline engine produces less power, but when combined with electric motors, the system’s total power can equalize or exceed that of a fossil fuel vehicle. The most efficient hybrids utilize "electric-only drive," allowing the vehicle to drive entirely on electricity and use less fuel. In hybrids that can't be plugged-in, electric-only drive is typically only utilized at low speeds and startup, enabling the gas or fossil-powered engine to operate at higher speeds, where it’s most efficient. Most plug-in hybrids, which tend to have larger batteries and motors, can drive entirely on electricity at relatively high speeds for extended distances.
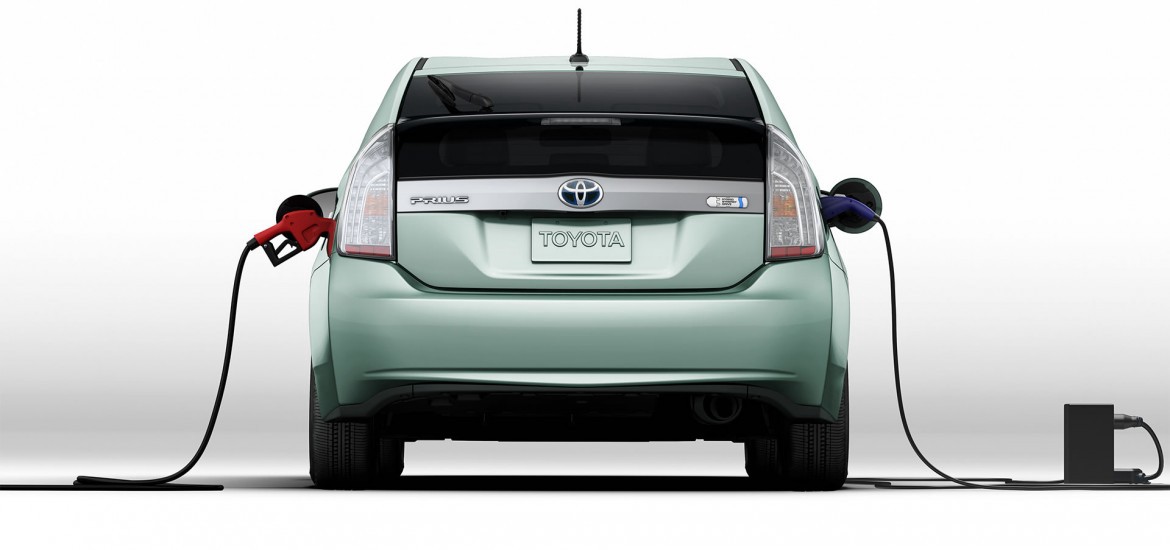

Hybrids that can't be recharged from an outlet aren't generally considered to be electric vehicles, as they rely exclusively on gasoline or fossil fuel for energy. Plug-in hybrids are considered electric vehicles, along with battery electric and hydrogen fuel cell vehicles. Electric vehicles only use an electric motor and battery, avoid fossil fuel engines altogether. Because they don't use gas or fossil fuel, electrics are often cleaner and cheaper to fuel than hybrids and fossil fuel vehicles. Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles power an electric motor and battery by converting stored hydrogen gas to electricity using a fuel cell. These vehicles are only beginning to come to market, but offer great potential as a low-carbon alternative to conventional cars and trucks as they have no tailpipe emissions, reduced global warming emissions, and can be refueled at a filling station similar to a gasoline vehicle.